A premature ventricular complex (PVC) is a premature beat arising from an ectopic focus within the ventricles. AKA: ventricular ectopics, ventricular extrasystoles, ventricular premature beats, ventricular premature depolarisations.
ECG features of PVCs
- Broad QRS complex (≥ 120 ms) with abnormal morphology
- Premature — i.e. occurs earlier than would be expected for the next sinus impulse
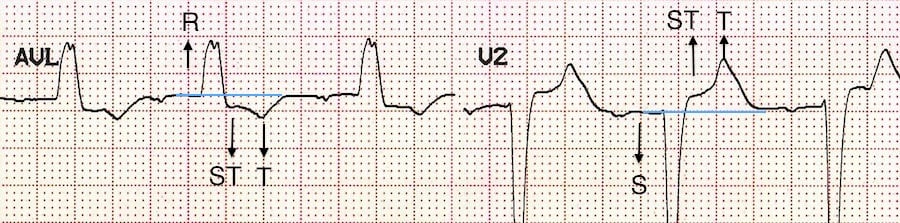
- Discordant ST segment and T wave changes.
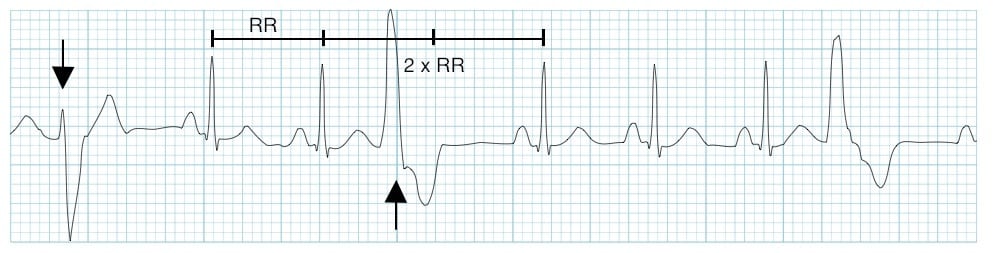
- Usually followed by a full compensatory pause
- Retrograde capture of the atria may or may not occur
Origin of Ectopic Beats
- Groups of pacemaker cells throughout the conducting system are capable of spontaneous depolarisation
- The rate of depolarisation decreases from top to bottom: fastest at the sinoatrial node; slowest within the ventricles
- Ectopic impulses from subsidiary pacemakers are normally suppressed by more rapid impulses from above
- However, if an ectopic focus depolarises early enough — prior to the arrival of the next sinus impulse — it may “capture” the ventricles, producing a premature contraction
- Premature contractions (“ectopics”) are classified by their origin — atrial (PACs), junctional (PJCs) or ventricular (PVCs)
Electrophysiology of Ventricular Ectopics
- Ectopic firing of a focus within the ventricles bypasses the His-Purkinje system and depolarises the ventricles directly
- This disrupts the normal sequence of cardiac activation, leading to asynchronous activation of the two ventricles
- The consequent interventricular conduction delay produces QRS complexes with prolonged duration and abnormal morphology
Discordance
Appropriate discordance describes a pattern of repolarisation abnormality (typically seen with left bundle branch block, paced rhythms, VT) in which the ST segment and T wave are directed opposite to the main vector of the QRS complex. Because there is abnormal depolarisation, there is subsequent abnormal repolarisation which is discordant:
- ST depression and T wave inversion in leads with a dominant R wave
- ST elevation with upright T waves in leads with a dominant S wave
With a full compensatory pause, the next normal beat arrives after an interval that is equal to double the preceding R-R interval
Retrograde capture describes the process whereby the ectopic impulse is conducted retrogradely through the AV node, producing atrial depolarisation. This is visible on the ECG as an inverted P wave (“retrograde P wave“), usually occurring after the QRS complex.
PVCs are said to be “frequent” if there are more than 5 PVCs per minute on the routine ECG, or more than 10-30 per hour during ambulatory monitoring.
Classification
PVCs may be either:
- Unifocal — arising from a single ectopic focus; each PVC is identical
- Multifocal — arising from two or more ectopic foci; multiple QRS morphologies
The origin of each PVC can be discerned from the QRS morphology:
- PVCs arising from the right ventricle have a left bundle branch block morphology (dominant S wave in V1)
- PVCs arising from the left ventricle have a right bundle branch block morphology (dominant R wave in V1)
PVCs often occur in repeating patterns:
- Bigeminy — every other beat is a PVC
- Trigeminy — every third beat is a PVC
- Quadrigeminy — every fourth beat is a PVC
- Couplet — two consecutive PVCs
- NSVT — between three and thirty consecutive PVCs (see below)
Clinical Significance
- PVCs are a normal electrophysiological phenomenon not usually requiring investigation or treatment
- Frequent PVCs may cause palpitations and a sense of the heart “skipping a beat”
- In patients with underlying predispositions (e.g. ischaemic heart disease, WPW), a PVC may trigger the onset of a re-entrant tachydysrhythmia — e.g. VT, AVNRT, AVRT
Frequent PVCs are usually benign, except in the context of an prolonged QTc, when they may predispose to malignant ventricular arrhythmias such as Torsades de Pointes by causing “R on T” phenomenon
Causes
Frequent or symptomatic PVCs may be due to:
- Anxiety
- Sympathomimetics
- Beta-agonists
- Excess caffeine
- Hypokalaemia
- Hypomagnesaemia
- Digoxin toxicity
- Myocardial ischemia
Example ECGs
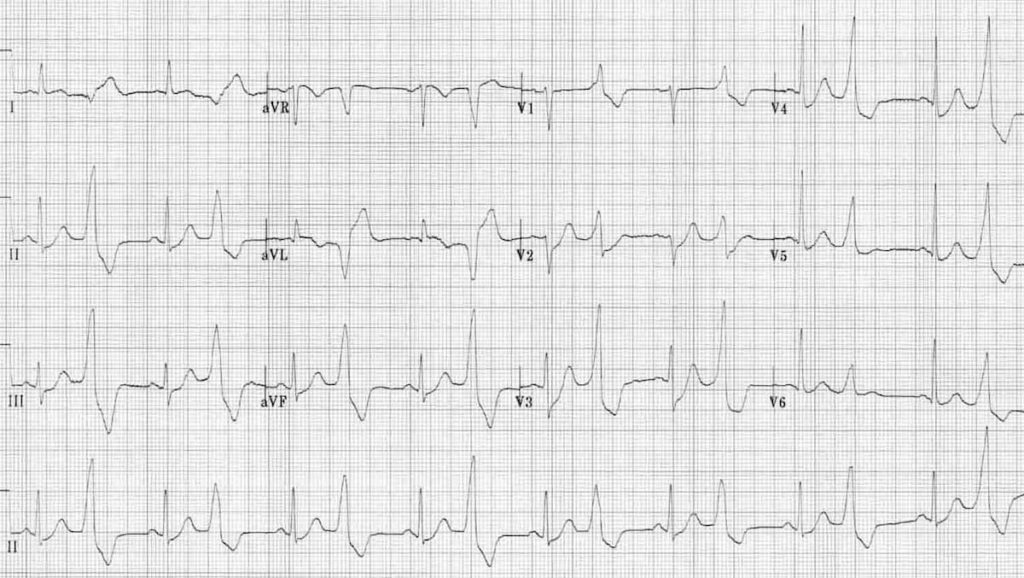
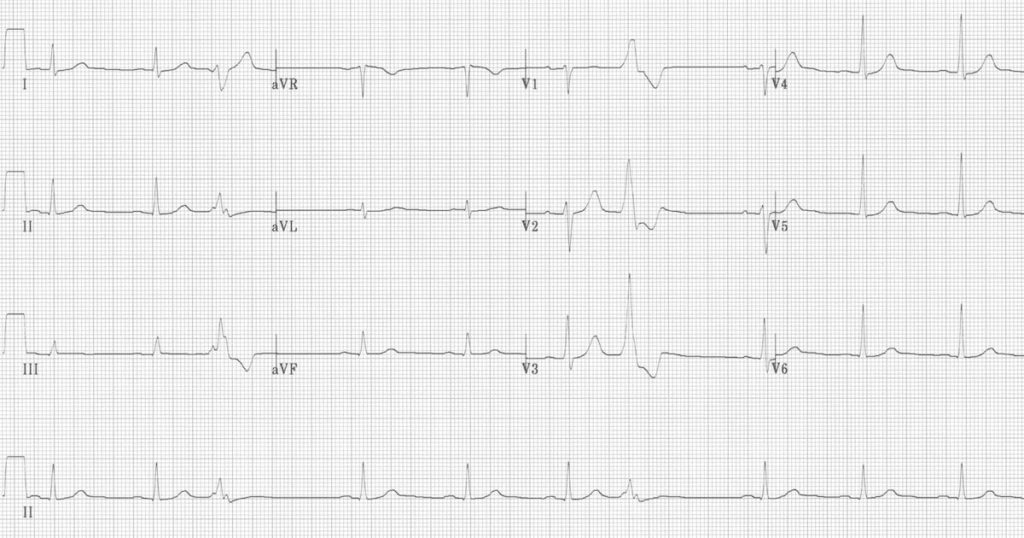
Multifocal PVCs
- Sinus rhythm with PVCs of two different morphologies (arrows)
- Note the appropriately discordant ST segments / T waves
- The pause surrounding the PVC is equal to double the preceding R-R interval (= a full compensatory pause)
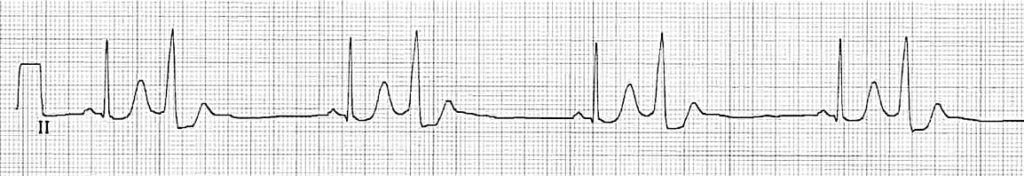
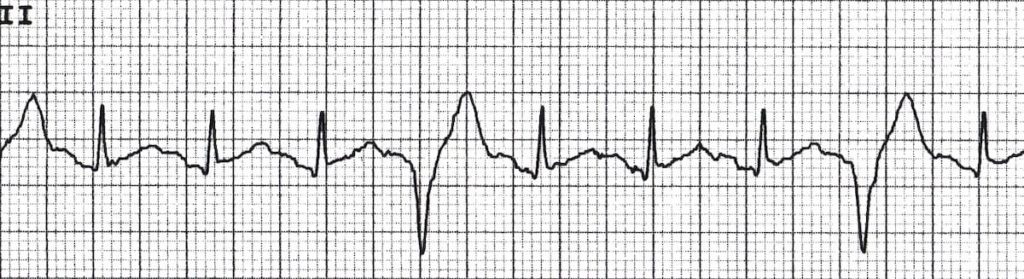
Ventricular bigeminy
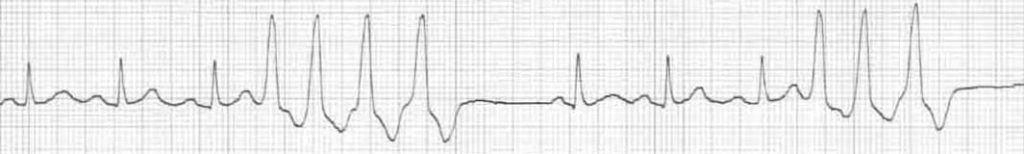
Ventricular quadrigeminy
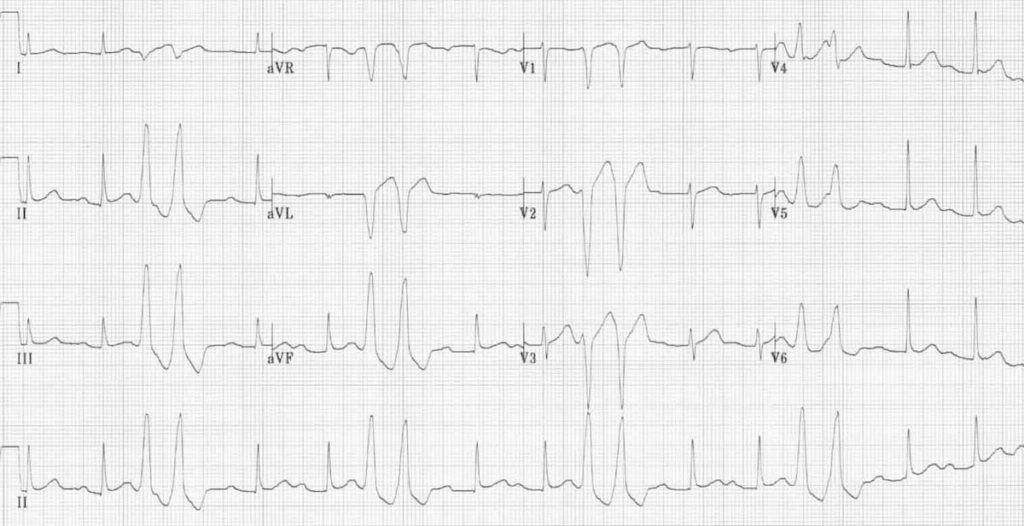
PVC pairs (couplets)
Non-sustained VT (NSVT)
When is a PVC not a PVC?
- Definitions vary regarding 3 or more PVCs
- Some authors define three PVCs as a triplet of PVCs; whilst others describe this as a ‘short burst of VT’; but more commonly as NSVT
- A consensus definition would be: 3-30 consecutive PVCs with a rate >100bpm described as non-sustained VT (ventricular rhythm if rate <100bpm)
No comments:
Post a Comment