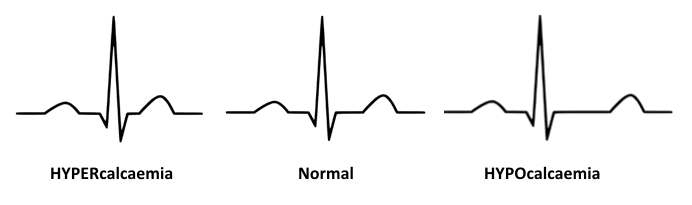
Hypocalcaemia
ECG changes in Hypocalcaemia
- Hypocalcaemia causes QTc prolongation primarily by prolonging the ST segment
- The T wave is typically left unchanged
- Dysrhythmias are uncommon, although atrial fibrillation has been reported
- Torsades de pointes may occur, but is much less common than with hypokalaemia or hypomagnesaemia
Hypocalcaemia Overview
- Normal serum corrected calcium = 2.2 – 2.6 mmol/L.
- Mild-moderate hypocalcaemia = 1.9 – 2.2 mmol/L.
- Severe hypocalcaemia = < 1.9 mmol/L.
Causes of Hypocalcaemia
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Acute pancreatitis
- Hyperphosphataemia
- Hypomagnesaemia
- Diuretics (frusemide)
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Congenital disorders (e.g. DiGeorge syndrome)
- Critical illness (e.g. sepsis)
- Factitious (e.g. EDTA blood tube contamination)
Symptoms of Hypocalcaemia
- Neuromuscular excitability
- Carpopedal spasm
- Tetany
- Chvostek sign
- Trousseau sign
- Seizures
ECG Examples
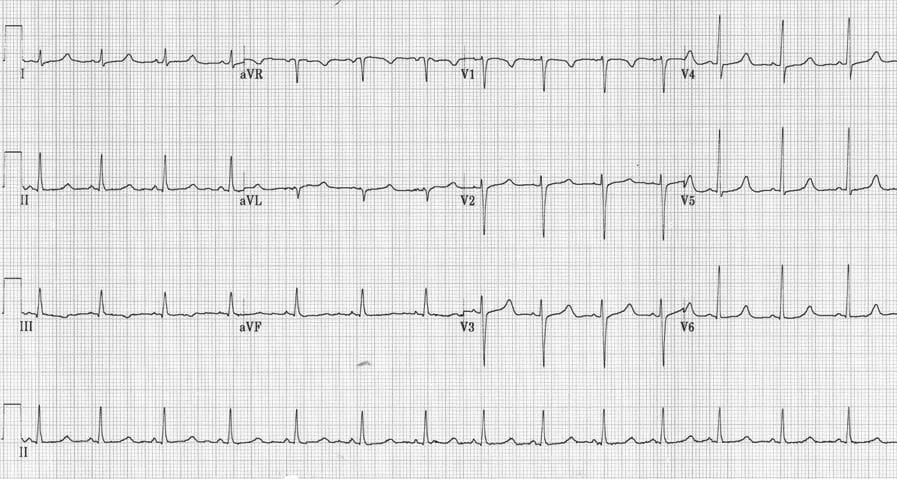
Example 1
Hypocalcaemia:
- QTc 500ms in a patient with hypoparathyroidism (post thyroidectomy) and serum corrected calcium of 1.40 mmol/L
- Reproduced from Nijjer et al. (2010)
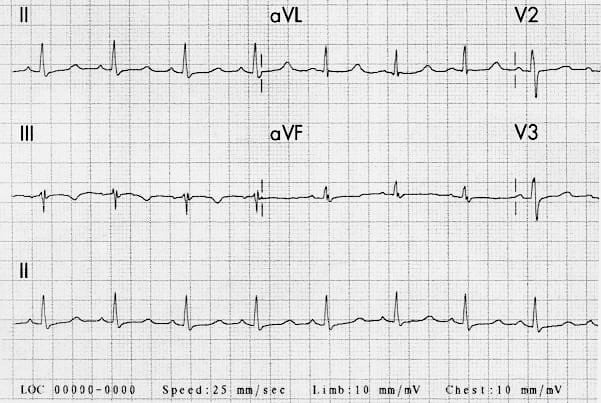
Example 2
Hypocalcaemia:
- QT prolongation in a patient with DiGeorge’s syndrome and serum calcium of 1.32 mmol/L
- Reproduced from Kar et al. (2005)
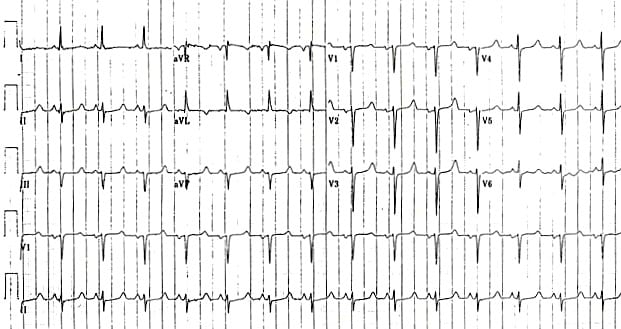
Example 3
- Hypocalcaemia causing a long QTc (510ms)
No comments:
Post a Comment